Advancing Research with Alzheimer's Disease Specific iPSC-Derived Cell Lines
World Alzheimer's Month

In recognition of World Alzheimer's Month, we proudly present our collection of Alzheimer-specific cell lines, resources related to Alzheimer’s Disease research, and more.
Understanding Alzheimer's Disease Through iPSC-Derived Cells
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of people globally. As we strive to unravel its mysteries, the general application of iPSC-derived cells in AD research has proven invaluable.
- Versatile Cellular Models: iPSC-derived cells offer a flexible platform, adaptable to various research needs. They can be differentiated into numerous neuronal types, providing a broader perspective on brain function and dysfunction.
- Disease Mechanism Insights: By studying how these cells interact and respond in different environments, researchers can gain insights into potential triggers and pathways involved in AD.
- Drug Response Evaluation: Using iPSC-derived cells, researchers can assess how potential treatments might interact with various neuronal types, paving the way for more comprehensive drug evaluations.
Explore our range of products and delve into the diverse applications of iPSC-derived cells in AD research.
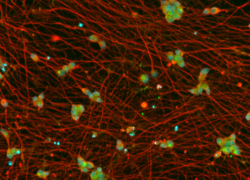
Day 7: Quick-Neuron™ Excitatory Neurons
Healthy Control
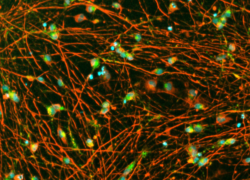
Day 7: Quick-Neuron™ Excitatory Neurons
Alzheimer's Disease Patient
The Significance of Alzheimer's Specific Cell Lines
For a more targeted approach in Alzheimer's research, cell lines derived specifically from AD patients stand out, offering unparalleled advantages.
- Genetic Uniformity: These cell lines encapsulate the genetic nuances of AD, ensuring consistent and highly relevant research outcomes.
- Disease Modeling: These cells provide a microscopic view of AD, allowing researchers to closely study and understand the disease's progression at the cellular level.
- High Throughput Screening: Tailored for AD, these cell lines are optimized for high-throughput drug screening, accelerating the journey towards potential treatments.
With our collaboration with the California Institute of Regenerative Medicine (CIRM), we tap into a vast reservoir of patient-derived iPSCs, ensuring our research remains at the forefront of AD-specific studies.
Our Alzheimer's Cell Line Collection
Our licensing agreement with CIRM’s iPSC Repository gives us access to over 1600 cell lines derived from patients with a variety of diseases, including Alzheimer's Disease (AD). Key features of our cell lines include:
- Diverse Range: From early to late-stage disease models.
- Genetic Background: Cell lines with APOE carrier information.
- Clinical information: Comprehensive data sheets and research background for each cell line.
Patient history information can be found under Resources.
| Line ID | Patient History | Gender | Sampling age | Race | On-set age | APOE Carrier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CW50114 | Link | F | 72 | Caucasian, not Latino | 65 | Yes (APOE Genotype 3/4) |
| CW50025 | Link | F | 68 | Caucasian, not Latino | 57 | Yes |
| CW50113 | Link | M | 68 | Caucasian, not Latino | 52 | Yes |
| CW50115 | Link | F | 67 | Caucasian, Latino | 58 | Yes |
| CW50137 | Link | F | 70 | Caucasian, not Latino | 62 | Yes |
| CW50147 | Link | M | 71 | Caucasian, not Latino | 62 | Yes |
| CW50104 | Link | M | 79 | Caucasian, not Latino | 73 | Yes |
| CW50107 | Link | M | 72 | Caucasian, not Latino | 65 | Yes |
| CW50169 | Link | F | 68 | Caucasian, not Latino | Unknown | |
| CW50170 | Link | F | 64 | Caucasian, not Latino | Unknown | |
| CW50173 | Link | F | 74 | Caucasian, not Latino | Unknown | |
| CW50175 | Link | F | 77 | Caucasian, not Latino | Unknown | |
| CW50176 | Link | M | 74 | Caucasian, not Latino | Yes | |
| CW50177 | Link | F | 85 | Caucasian, Latino | Unknown |
Our Alzheimer's Disease Products
| Cat No. | Product Name | Disease StatusDescription |
|---|---|---|
| EX-SeV-AD | Quick-Neuron™ Excitatory - Human iPSC-derived Neurons (Alzheimer's Disease) | Alzheimer's Disease Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived excitatory neurons from Alzheimer's Disease patient |
| CH-SeV-AD | Quick-Neuron™ Cholinergic - Human iPSC-derived Neurons (Alzheimer's Disease) | Alzheimer's Disease Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived cholinergic neurons from Alzheimer's Disease patient |
| AS-SeV-AD | Quick-Glia™ Astrocytes - Human iPSC-derived Astrocytes (Alzheimer's Disease) | Alzheimer's Disease Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived astrocytes from Alzheimer's Disease patient |
| MT-SeV-AD | Quick-Neuron™ Motor - Human iPSC-derived Neurons (Alzheimer's Disease) | Alzheimer's Disease Cryopreserved human iPSC-derived motor neurons from Alzheimer's Disease patient |
Alzheimer’s Disease Resources
Explore our curated resources in honor of World Alzheimer's Month. Dive into our insightful webinar on Alzheimer's Disease, gain knowledge from our detailed application note on AD modeling, and don't miss out on our exclusive promotions tailored for this significant month.
WEBINAR
iPSCs & Microfluidics: Innovative Approaches for Modeling Alzheimer's Disease
This past World Alzheimer's Month, we put on our most recent webinar "iPSCs & Microfluidics: Innovative Approaches to Modeling Alzheimer's Disease," in collaboration with Ananda Devices. View the recording and dive deep into the exciting topics of iPSC-derived, patient-specific cells and microfluidics platforms, two tools that are helping to make strides in the world of Alzheimer's research.
- Streamed Live: Friday, September 22nd, 2023
- Speakers:
- Margaret Magdesian, Ph.D. from ANANDA Devices
- Michal Millrod, Ph.D. from Elixirgen Scientific
- Topics:
- Utilizing iPSC-derived cells for modeling AD
- Microfluidics platforms and their applications in AD research
- Discussion
- Animal Models vs. Patient-Derived Models
- Variability Between Patient Lines
- Q&A
For more information on ANANDA Devices, their technology, or their product offerings, please visit Ananda Devices' LinkedIn page.
APPLICATION NOTE
Modeling Alzheimer’s Disease with ELISA and Off-the-Shelf Patient iPSC-Derived Neurons
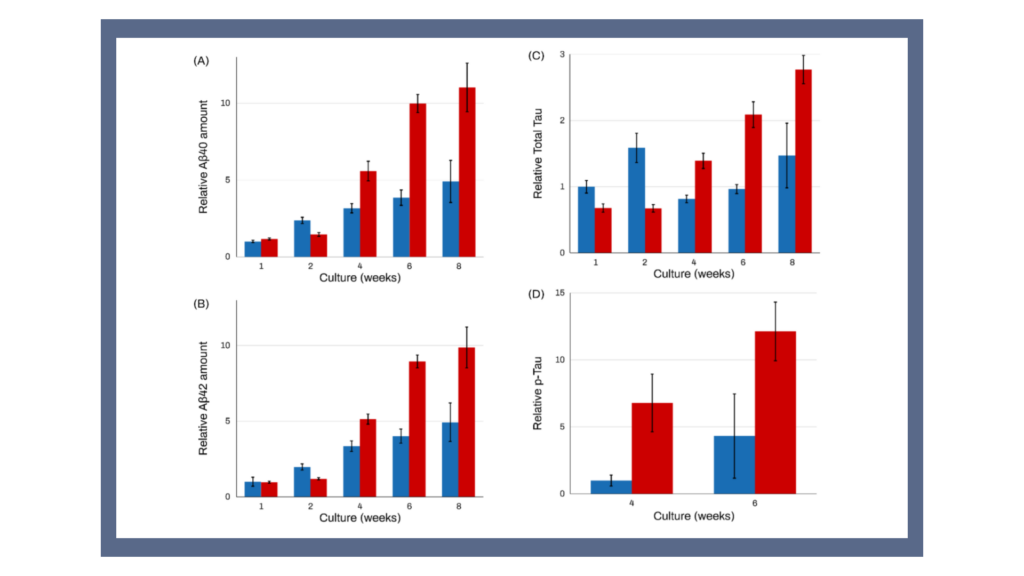
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) remains a significant challenge in neurodegenerative research. Our most recent Application Note provides a detailed guide, aiming to equip the scientific community with the latest tools and methodologies for modeling AD.
Dive into Our Application Note to Explore:
- The Potential of ELISA: An invaluable technique for the detection and measurement of key AD biomarkers such as Aβ42, Aβ40, total Tau, and p-Tau.
- The Breakthrough of iPSC-Derived Neurons: Understand the significance of our neurons derived from AD patient iPSCs, and how they display known phenotypes of AD.
- Drug Discovery & Beta-Secretase: Learn about the role of β-secretase inhibitors in reducing the production of Aβ peptides, showcasing the application of our model in potential treatment avenues.
PROMOTION
World Alzheimer's Month Specials
In honor of World Alzheimer's Month, we are offering exclusive promotions:
- Discounted Rates: Enjoy 20% off of product purchases when you include Alzheimer’s Disease patient lines with a healthy control*
- Bundled Offers: Buy a large differentiation kit, get 1 small differentiation kit for FREE**
- Service Offers: Discounts on AD-specific service projects***