Quick-Muscle Skeletal – SeV Complete Kit used in Molecular Therapy paper
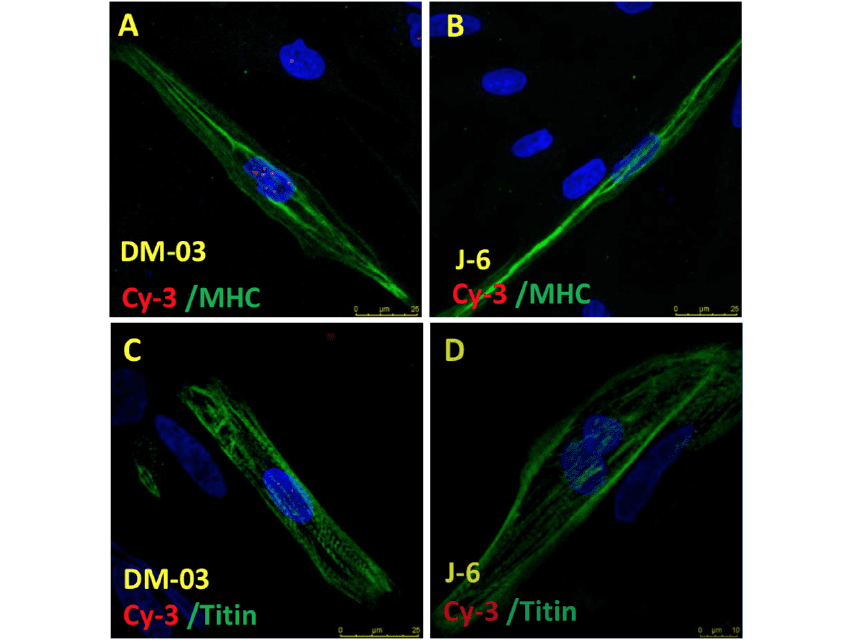
BALTIMORE, January 29, 2019 – Elixirgen Scientific’s Quick-Muscle™ Skeletal – SeV Complete Kit (QMS-SeV) was used in a paper that was recently published in Molecular Therapy. Dr. Guangbin Xia (University of New Mexico)’s publication, “Therapeutic Genome Editing for Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9” presents his results using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing and induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology towards a potential therapeutic approach for Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1). Dr. Xia’s team established DM1 patient iPSC cell lines, and then used CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing to treat those patient iPSC cell lines. They then differentiated both untreated and treated DM1 patient iPSC cell lines into skeletal muscle cells using Elixirgen Scientific’s commercially available QMS-SeV kit to confirm the lack of disease phenotype in the treated cell lines. Dr. Xia’s team was able to take advantage of the QMS-SeV kit’s fast, seven-day differentiation protocol and high differentiation efficiency to produce his data. They saw disease phenotype reversal in the differentiated skeletal muscle fibers, and his positive results show promise for use in future therapeutics genome editing for DM1. The Elixirgen Scientific team is excited to assist his successful publication and the role that the Quick-Muscle™ Skeletal – SeV Complete Kit played in accelerating his research.
Elixirgen Scientific’s Quick-Muscle™ Skeletal – SeV Complete Kit is available for order through the company web store at /store/. The company also offers differentiation kits for mixed neurons (a mixture of multiple neuron types), dopaminergic neurons, GABAergic neurons, and cholinergic neurons, as well as already-differentiated neurons and other tissues generated from patient and control iPSCs from the CIRM iPSC repository. For details of CIRM iPSC repository, click this link.
For more information about the publication, please click the link below:
https://www.cell.com/molecular-therapy-family/molecular-therapy/fulltext/S1525-0016(18)30444-1
"Therapeutic Genome Editing for Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 Using CRISPR/Cas9" by Y. Wang, et. al. is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0